Unlocking the Artistry of Pantographs for Drawing: A Detailed Exploration


Science Fun Facts
In the realm of drawing, a fascinating tool called a pantograph plays a crucial role. This intricate device enables artists to replicate or scale images with remarkable precision and accuracy by linking two different points. Imagine the innovation that sparked this creation, amplifying the artist's ability to visualize and create intricate designs on paper. Each stroke and curve meticulously traced through the mechanics of the pantograph, showcasing a blend of artistry and engineering unlike any other.
Discover the Wonders of Science
Diving deep into the world of pantographs for drawing unveils a treasure trove of historical significance and modern-day applications. This tool, once considered avant-garde, has withstood the test of time in contemporary artistic practices. Unlock the secrets of how pantographs have transcended generations, evolving from a mere mechanical contraption to an indispensable instrument in the artist's toolkit. Delve into a journey that elucidates the magic of this device, revolutionizing the landscape of drawing with its precision and adaptability.
Science Quiz Time
Engage in an interactive exploration of the pantograph's ingenuity through thought-provoking questions and brain teasers. What fundamental principles underlie the functionality of a pantograph for drawing? Test your knowledge on the mechanisms that drive this tool's precision and efficiency. Challenge yourself with multiple-choice questions that spotlight the diverse applications of pantographs across various artistic fields. Embrace the learning journey with gamification that enhances understanding and appreciation for the intricate science behind drawing innovation.
Science Experiment Showcase
Embark on a hands-on experience by conducting a scientific experiment that mirrors the essence of a pantograph. Explore the relationship between pivot points and tracing arms to comprehend the mechanics of replication and scaling. With step-by-step instructions and a detailed materials list, recreate the magic of a pantograph in a safe and engaging setting. Prioritize safety tips and precautions to ensure a successful experiment that bridges the gap between art and science, immersing you in the marvels of technical creativity.
Introduction to Pantograph for Drawing
This segment serves as a crucial foundation for understanding the mechanics and applications of pantographs in the realm of drawing. Delving into the intricacies of pantograph usage, we will explore how this device has been instrumental in revolutionizing precision and creativity in art and design, engineering, architecture, education, and science. Through a detailed analysis of the basics, mechanics, types, and modern innovations of pantographs, readers will gain a comprehensive insight into the multifaceted nature of these tools and their relevance in various fields.
Understanding the Basics
Definition of a Pantograph
Embarking on our journey into the world of pantographs, we first elucidate the core concept of a pantograph. Defined as a mechanical linkage system, the pantograph enables the replication of drawings or images in a scaled manner. This fundamental aspect of a pantograph is pivotal in achieving precise reproductions, making it a popular choice among artists and engineers alike. A key feature of the pantograph's design is its ability to maintain proportional accuracy when copying or resizing images, providing users with a versatile tool for artistic and technical endeavors.
Historical Evolution
Tracing the historical evolution of pantographs unveils a captivating narrative of innovation and adaptation. From its origins as a manual drafting aid to its modern-day digital iterations, the pantograph has undergone significant advancements over the centuries. The historical significance of the pantograph lies in its transformative impact on the fields of art, engineering, and education, facilitating intricate design work and efficient teaching methodologies. Despite its numerous advantages, the evolution of pantographs has also encountered challenges, shaping the device's design and functionality over time.
Key Components
Exploring the key components that constitute a pantograph unveils the meticulous craftsmanship behind its operation. The integration of linkages, arms, and tracing mechanisms forms the backbone of a pantograph's functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and accurate transfer of images or designs, highlighting the precision engineering employed in pantograph construction. While the complexity of key components may pose maintenance challenges, they are essential in achieving the desired results in both artistic and technical applications.
Mechanics Behind Pantograph
Linkage System
A critical aspect of pantograph mechanics lies in its intricate linkage system, which governs the movement and scaling of the device. By leveraging a series of interconnected links, the pantograph can accurately reproduce images at varying sizes, ensuring uniformity in design replication. The linkage system's flexibility and adjustability enhance the versatility of the pantograph, allowing users to customize scaling ratios according to their specific requirements.
Scaling Principles
Central to the operation of a pantograph are the scaling principles that dictate how drawings are resized or reproduced. By adhering to mathematical scaling formulas, the pantograph ensures that proportions are maintained during the replication process. This adherence to scaling principles is essential for achieving accurate and consistent results, making the pantograph a reliable tool for achieving precision in design work.
Working Mechanism
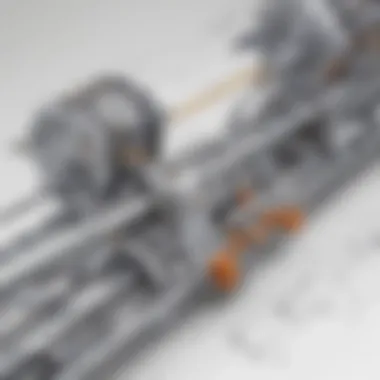

The working mechanism of a pantograph encompasses the intricate interplay of its components to facilitate image transfer. As users maneuver the tracing stylus over a reference image, the pantograph's arms and linkages work cohesively to replicate the drawing on a different scale. This seamless coordination of movement and translation is essential for achieving fidelity in design reproduction, highlighting the effectiveness of the pantograph's working mechanism.
Types of Pantographs
Reduction Pantograph
One of the primary types of pantographs is the reduction pantograph, which enables users to create smaller reproductions of original drawings. By adjusting the arm lengths and pivot points, the reduction pantograph offers a versatile solution for scaling down designs with precision. This type of pantograph is particularly useful in art and design, where intricate details need to be accurately replicated on a smaller scale.
Copying Pantograph
In contrast, the copying pantograph excels in reproducing exact replicas of original drawings without altering their size. This type of pantograph maintains a one-to-one ratio between the reference image and the reproduced copy, making it an essential tool for duplicating intricate designs with utmost accuracy. Engineers and architects often utilize copying pantographs to create blueprint reproductions and precise technical drawings.
Enlarging Pantograph
For tasks that require scaling up original designs, the enlarging pantograph offers a practical solution for achieving larger reproductions. By adjusting the pivot points and arm lengths in a controlled manner, users can enlarge drawings while preserving their proportions. This type of pantograph is valuable in creating scaled-up models, architectural plans, and detailed presentations that require meticulous enlargement.
Applications in Various Fields
Exploring the utilization of pantographs across various fields is crucial in understanding their versatile applications. In this article, we will delve into the significance of pantographs in art, design, engineering, architecture, education, and science. Pantographs play a pivotal role in these fields by enabling precise drawings, blueprint reproduction, complex designs, artistic adaptations, concept visualization, and STEM learning.
Art and Design
Creating Replicas
When it comes to creating replicas, pantographs offer a unique advantage. It allows artists to replicate intricate designs with exceptional precision, preserving every detail of the original artwork. The key characteristic of creating replicas with pantographs lies in its ability to scale down or enlarge images without compromising accuracy. This feature is highly beneficial for artists looking to mass-produce their works or create consistent copies. Despite its advantages in maintaining consistency and precision, a potential downside of using pantographs for replica creation is the limitation in reproducing textures and complex brushwork.
Precision Drawing
Precision drawing with pantographs elevates the accuracy and detail in artworks. Artists can achieve incredibly precise lines and measurements by utilizing pantographs in their creative process. The key characteristic of precision drawing is the strict geometric control it offers, ensuring that every stroke is replicated faithfully. This level of precision is particularly valuable in technical drawings and highly detailed illustrations. However, the drawback of precision drawing using pantographs is the time-consuming nature of setting up the apparatus and adjusting the scales for each project.
Artistic Adaptations
Artistic adaptations through pantographs allow artists to reinterpret existing artworks in a personalized manner. This process involves taking inspiration from established designs and incorporating one's artistic flair. The key characteristic of artistic adaptations lies in the seamless integration of the original concept with the artist's unique style. This approach opens up endless possibilities for creative exploration and artistic experimentation. While this method offers great flexibility and creative freedom, artists may face criticism for lack of originality or creative dependency on existing works.
Engineering and Architecture
Blueprint Reproduction
Pantographs excel in blueprint reproduction by facilitating the accurate duplication of technical drawings. Architects and engineers rely on pantographs to reproduce blueprints with precise scaling, ensuring that every detail is replicated faithfully. The key characteristic of blueprint reproduction using pantographs is the ability to resize architectural plans without manual calculations, saving time and reducing human errors. This feature is highly beneficial for ensuring consistency and accuracy in large-scale construction projects. However, one potential drawback of blueprint reproduction with pantographs is the complexity involved in adapting the technology to digital drafting software.
Complex Designs
Employing pantographs for creating complex designs opens up a realm of creative possibilities. Designers can intricately replicate intricate patterns and geometric shapes with meticulous detail. The key characteristic of using pantographs for complex designs is the ability to maintain symmetry and precision in elaborate structures. This capability is particularly valuable in architectural projects and product design requiring intricate detailing. However, the challenge with complex designs lies in setting up the pantograph equipment correctly and managing the intricate adjustments required for each design iteration.
Modeling


Pantographs are indispensable in modeling tasks, aiding in the precise creation of three-dimensional prototypes. Engineers and designers utilize pantographs to scale down or enlarge models accurately, capturing every detail of the original design. The key characteristic of modeling with pantographs is the efficient translation of design concepts into tangible models with high precision. This feature is instrumental in testing concepts, evaluating form and function, and presenting visual representations of complex ideas. Despite its advantages, one limitation of modeling with pantographs is the potential margin of error introduced during the calibration and tracing processes.
Education and Science
Demonstrations
In educational settings, pantographs serve as valuable tools for demonstrating principles of geometry and proportion. Teachers use pantographs to showcase scale modifications and proportional relationships, aiding students in understanding mathematical concepts visually. The key characteristic of demonstrations with pantographs is the interactive and engaging way of visualizing abstract ideas. This hands-on approach fosters a deeper comprehension of spatial relationships and mathematical principles. However, the downside of relying on pantographs for demonstrations is the requirement for precise adjustments and calibration to ensure accurate representations.
Concept Visualization
Concept visualization with pantographs enhances the communication of ideas and designs in scientific and educational contexts. Researchers and educators utilize pantographs to illustrate complex concepts in a simplified visual format, aiding in knowledge retention and comprehension. The key characteristic of concept visualization using pantographs is the ability to transform abstract theories into tangible visual representations. This visual aid facilitates learning and empowers students to grasp complex concepts more effectively. Nevertheless, the challenge in concept visualization lies in ensuring that the scale and proportions are accurately represented to avoid misconceptions.
STEM Learning
Pantographs play a significant role in STEM learning, providing hands-on experiences for students in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. By using pantographs, students can explore fundamentals of geometry, scaling principles, and spatial reasoning in a practical way. The key characteristic of STEM learning with pantographs is the enhancement of problem-solving and critical thinking skills through real-world applications. This experiential approach fosters a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and encourages students to engage actively in the learning process. However, a potential drawback of incorporating pantographs in STEM education is the initial learning curve required to operate the equipment effectively and understand its mechanisms.
Modern Innovations and Advancements
In this section, we delve into the realm of modern innovations and advancements related to pantographs for drawing. The integration of technology has played a pivotal role in revolutionizing how pantographs are utilized in various fields. Through the incorporation of digital pantographs, artists and designers can enhance their precision and creativity like never before. The advent of digital pantographs has brought forth a new era of advancements, offering unparalleled benefits and considerations for users.
Digital Pantographs
Integration of Technology
Discussing the integration of technology within the realm of pantographs is crucial for understanding its transformative impact. The seamless fusion of digital interfaces with traditional pantograph mechanisms has streamlined the drawing process and elevated accuracy levels. By harnessing technological integration, artists can achieve meticulous detail and intricate designs with exceptional ease. The key characteristic of technology integration lies in its ability to bridge the gap between manual artistry and digital precision, making it a popular choice among contemporary creators.
Enhanced Precision
Enhanced precision is a fundamental aspect of digital pantographs that distinguishes them from their traditional counterparts. Through advanced calibration and digitized measurements, digital pantographs ensure greater accuracy and consistency in reproduced drawings. This heightened precision empowers artists to execute complex designs with unmatched finesse, contributing to the enhancement of their craft. Despite some considerations regarding calibration and maintenance, the benefits of enhanced precision in digital pantographs outweigh any potential drawbacks.
Virtual Applications
The realm of virtual applications opens up a plethora of opportunities for artists utilizing pantographs in their creative pursuits. By leveraging virtual platforms, artists can explore innovative techniques and experiment with diverse styles in a digital environment. The unique feature of virtual applications lies in its capacity to simulate real-world drawing scenarios, offering a risk-free space for artistic exploration. While virtual applications come with distinct advantages such as accessibility and versatility, potential drawbacks may include a learning curve for users transitioning from traditional methods.
Future Prospects
Considering the future prospects of pantographs, the integration of artificial intelligence stands out as a game-changing element. The incorporation of AI algorithms in pantograph systems optimizes drawing processes and assists artists in achieving unparalleled levels of efficiency and accuracy.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence promises to revolutionize the field of drawing by enabling autonomous decision-making and pattern recognition within pantograph operations. The key characteristic of AI lies in its ability to analyze complex data and optimize drawing techniques based on learned patterns. This innovative feature makes AI a highly beneficial choice for advancing the capabilities of pantographs in various artistic applications.
Automation
Another pivotal aspect of future prospects is automation, which streamlines drawing processes and reduces manual intervention. By automating repetitive tasks, artists can focus on creativity and design aspects, fostering a more efficient workflow. The key characteristic of automation lies in its ability to enhance productivity and eliminate human error, making it a popular choice for artists seeking streamlined operations.


Customization
The concept of customization in pantographs opens up a world of possibilities for artists looking to tailor their drawing experience. With customizable settings and parameters, artists can personalize their workflow to suit their specific requirements and artistic preferences. The key characteristic of customization lies in its capacity to adapt to individual artistic styles, fostering creativity and self-expression. While customization offers immense benefits in enhancing user experience, considerations about complexity and compatibility with existing systems should be carefully evaluated.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the myriad benefits of modern innovations in pantographs, certain challenges and limitations persist, shaping the landscape of their usage in artistic endeavors.
Complexity
The complexity associated with integrating digital technologies into pantographs poses a significant challenge for users seeking seamless interactions. As systems become more intricate and feature-rich, users may encounter difficulties in navigating through various functionalities and settings. While complexity enhances the sophistication of pantograph capabilities, it also necessitates comprehensive training and technical expertise to leverage these advancements effectively.
Cost Factors
Cost factors play a crucial role in determining the accessibility and viability of modern pantograph systems for artists and designers. The initial investment in acquiring digital pantographs and maintaining their functionality can be substantial, potentially limiting access for emerging creators with budget constraints. Moreover, ongoing expenses related to software updates and equipment maintenance add to the overall cost considerations associated with utilizing advanced pantograph technologies.
Maintenance Issues
The maintenance of digital pantographs introduces a set of challenges related to system upkeep and technical support. Ensuring the optimal performance of digital components and addressing potential software glitches require dedicated maintenance protocols and resources. While digital pantographs offer enhanced capabilities and precision, the need for regular maintenance and troubleshooting can pose logistical challenges for users, impacting workflow efficiency and productivity.
Conclusion
The conclusion of this comprehensive guide on exploring the use of a pantograph for drawing is paramount in synthesizing the wealth of information presented. Understanding the historical significance, mechanics, and various applications of the pantograph allows for a profound appreciation of its role in art, engineering, and education. By delving into the nuances of pantograph technology, individuals can grasp the intricate linkages and scaling principles that underpin its functionality in producing precise drawings. Moreover, the exploration of modern innovations such as digital pantographs and the discussion of future prospects shed light on the evolving landscape of this tool. Acknowledging the challenges and limitations also provides valuable insights into improving and optimizing pantograph usage moving forward, enhancing its utility in diverse fields.
Summary of Key Points
Historical Significance
The historical significance of the pantograph lies in its revolutionary impact on the art of drawing. By tracing its evolution from early designs to modern adaptations, one can appreciate how this device has transformed artistic endeavors. The key characteristic of historical significance is its ability to democratize precision drawing, making complex designs more accessible to artists of varying skill levels. Despite some limitations in the past, the development of pantographs has greatly enhanced the creation of detailed replicas and artistic adaptations.
Diverse Applications
The diverse applications of the pantograph span across art, engineering, and education, showcasing its versatility and adaptability. From replicating blueprints with utmost precision to aiding in STEM learning through concept visualization, this tool has proven instrumental in various fields. The unique feature of diverse applications lies in its capacity to cater to a myriad of creative and technical needs, fostering innovation and efficiency. While some challenges exist, such as maintenance issues, the benefits of employing pantographs in diverse settings outweigh the drawbacks.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the future directions of pantograph technology hold promising prospects for integration with artificial intelligence and automation. By leveraging these advancements, users can expect enhanced precision and customization capabilities, further expanding the tool's potential. The key characteristic of future directions is the seamless fusion of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology, paving the way for new creative possibilities. While complexities may arise, the potential benefits of embracing these advancements far outweigh any initial obstacles.
Closing Thoughts
Impact on Artistic Endeavors
The impact of pantographs on artistic endeavors cannot be understated, as it has redefined the way artists approach precision drawing and replication. By streamlining complex processes and allowing for intricate details to be captured with ease, pantographs empower artists to channel their creativity more effectively. The key characteristic of this impact lies in its ability to bridge the gap between traditional artistry and technological innovation, fostering a dynamic landscape for artistic expression. While challenges like technological integration exist, the overall benefits for artists seeking to elevate their craft are indisputable.
Technological Integration
The integration of pantographs with technology represents a significant advancement in the field, offering artists and designers a versatile tool for enhancing their creative output. By utilizing digital platforms and virtual applications, users can transcend physical limitations to explore new artistic dimensions. The key characteristic of technological integration is its capacity to streamline workflows and enhance precision, making it a valuable asset for professionals. While some adjustment periods may be necessary, the long-term advantages of embracing technology in pantograph usage far exceed any initial hurdles.
Continued Relevance
Despite the evolution of drawing technologies, the continued relevance of pantographs persists due to their unique capabilities and adaptability. By remaining a staple tool in numerous industries, the pantograph demonstrates its enduring value in an ever-changing landscape. The key characteristic of its continued relevance is the time-tested efficiency and precision it offers, making it a reliable choice for professionals and enthusiasts alike. While challenges like cost factors may pose considerations, the sustained relevance of pantographs underscores their timeless appeal and importance in the realm of drawing tools.







