Discovering Geodes: Shapes, Textures, and More


Intro
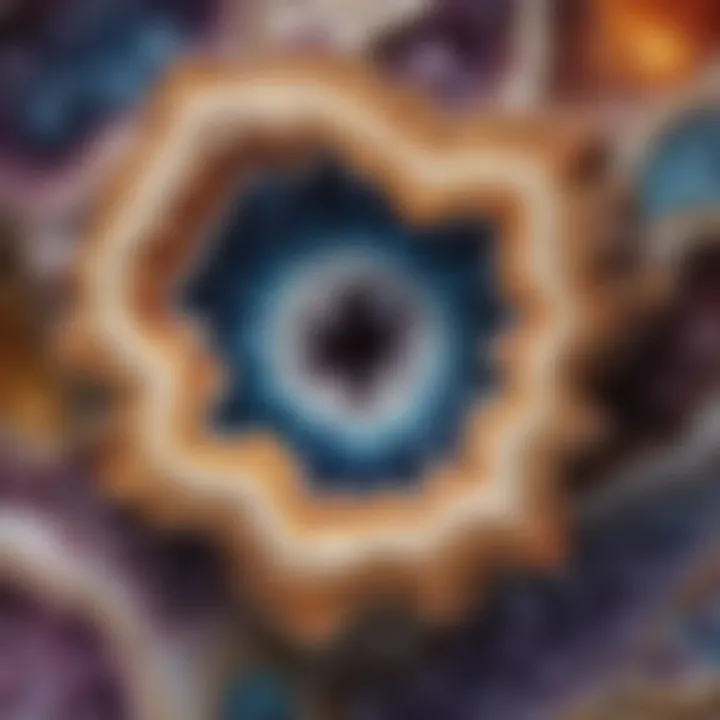
Geodes are much more than simple rocks. Their allure lies not only in their beautiful interiors but also in their outer features. This guide will take young science enthusiasts on a journey through the external characteristics of geodes. We will look at their shapes, textures, and structures, delving into how they are formed. Understanding these features can ignite curiosity about geology and nature.
Geodes are often round or oval, resembling eggs. Their surfaces can be smooth or rough, and sometimes they hold surprises inside. The way they are formed is a fascinating process involving minerals and time. This guide will provide exciting insights into what makes each geode unique.
Science Fun Facts
Interesting Trivia and Facts
- Did you know that geodes can be found all over the world? Places like Brazil, Mexico, and even some parts of the United States have stunning geodes.
- Some geodes are large enough to fit a person inside! Imagine walking into a giant geode—what a sight that would be.
- The crystals found within geodes can be made of quartz, amethyst, or even calcite. Each type gives a different look and feel.
Quirky Science Stories
There's a legend about geodes that they contain the spirits of rocks. People used to believe that by opening a geode, they could release the energy within. While this is just a story, it emphasizes how special many consider these formations.
Amazing Science Records
The largest geode ever discovered is known as the 'Pulpí Geode' in Spain. It has stunning gypsum crystals that can reach up to 12 meters long! Such dimensions allow for spectacular views, drawing in curious visitors.
"Geodes are nature's hidden treasures, waiting to be discovered."
Thought-Provoking Questions
- What do you think causes the different shapes and textures of geodes?
- How might the environment change the crystals that grow inside a geode over time?
- Why do you think people are so fascinated with looking inside geodes?
Discovering the Wonders of Science
Exploring Various Scientific Concepts
The formation of geodes relates closely to geology and mineralogy. Understanding these topics can help children appreciate the natural processes that create unique geological features. Learning about igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks can also enhance their knowledge about the Earth's history.
Educational Videos and Animations
Interactive videos are available online to show how geodes form. Websites like Britannica offer visual content that can engage young learners. These resources help visualize the stories behind geodes, making the scientific concepts easier to grasp.
Real-Life Applications of Science
Geology plays an essential role in everyday life, from construction to finding resources. Geodes also have artistic uses. Many artists incorporate geodes into jewelry, home decor, and sculptures, bringing the beauty of nature indoors.
Science Experiment Showcase
Fun and Engaging Experiments
Children can conduct simple experiments to explore the concept of crystal growth. By using sugar or salt, they can create their own 'geodes' at home. This practical activity not only makes science fun but reinforces what they learn.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Materials Needed:
- Instructions:
- Sugar or salt
- Water
- A clear container
- A stirring spoon
- String
- A pencil
- Start by boiling water in a pot.
- Add sugar or salt until it no longer dissolves (this is a saturated solution).
- Let it cool slightly, then pour it into a clear container.
- Tie a string to a pencil and place it in the solution so the string hangs inside.
- Wait for a few days as crystals grow!
Safety Tips and Precautions


Always ensure children are supervised when boiling water. Discuss safe handling of materials and remind them to wash their hands after conducting experiments.
This guide will take young readers through the intriguing world of geodes and their external features, moving them closer to understanding and appreciating the sciences around them.
Prolusion to Geodes
Geodes are among the most captivating natural wonders found on our planet. Their intriguing appearance often sparks curiosity in people of all ages, especially young learners. Understanding geodes involves looking closely at their external features. This includes their unique shapes, textures, and colors.
Definition of Geodes
A geode is a hollow rock formation that contains mineral crystals. On the outside, a geode may look unremarkable, resembling an ordinary stone. However, when opened, it reveals a stunning inner structure. The process that creates geodes occurs in volcanic or sedimentary environments. The minerals slowly accumulate over time inside the rock, forming beautiful crystals. The formation process can take thousands, or even millions, of years.
Importance of Understanding Geodes
Learning about geodes is important for several reasons. First, they offer insights into geological processes that shaped our planet. Understanding how they form can help children learn about earth science. Second, studying geodes encourages observation and curiosity about nature. This can lead to a deeper appreciation for the environment. Lastly, geodes can inspire future scientists. They serve as a bridge to understanding larger concepts in geology and mineralogy.
"Geodes remind us of the beauty that nature can create over time, revealing treasures in unexpected places."
Overall, the study of geodes is not just about rocks. It is about exploring the stories told by the earth itself.
Common External Characteristics of Geodes
Understanding the common external characteristics of geodes is key to appreciating their uniqueness. Geodes can be found in various environments, such as volcanic and sedimentary settings, each contributing to their distinctive features. By observing these characteristics, one can gain insights into the geological processes that created them, enhancing our understanding of Earth's history.
Shape and Size Variability
Geodes are notable for their diverse shapes and sizes. Some can be as small as a marble, while others may reach well over a meter in diameter. Shape variability is a product of the geological conditions under which they formed. Factors such as the space where minerals deposited and the surrounding matrix influence their final forms. Most geodes are spherical or ovoid, but they can also exhibit more irregular shapes.
Observing the size and shape can tell enthusiasts a lot about the geode. For young explorers, assessing these elements can be an exciting and educational experience. They can learn about the geological environments that lead to such variability, stimulating curiosity about rocks and minerals.
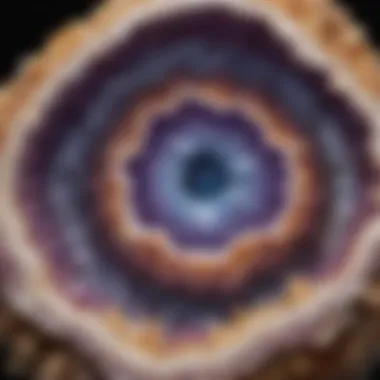
Surface Texture and Patterns
When examining geodes, the surface texture can often captivate the observer. The textures can range from smooth and glossy to rough and jagged. Some geodes might display interesting patterns like ridges or bumps. These textures arise from the mineral deposits lining the inner cavity.
Patterns can also be traced back to how the mineral crystals grew inside. For instance, a geode with quartz crystals might shimmer with a glassy appearance, while one with calcite can present a softer, more rounded texture.
Children can engage in tactile exploration of different geodes to feel these textures, making the learning process tangible. By understanding surface characteristics, they can appreciate how Earth's processes shape not just the inside, but also the outside of these fascinating formations.
Coloration and Variability
Color is perhaps one of the most striking external characteristics of geodes. The colors can range from clear whites to rich violets, deep blues, vibrant reds, and earthy browns. This diversity results from the different minerals involved in each geode's formation. For example, the presence of iron can lead to red or brown hues, while manganese might yield purples or pinks.
The appearance of color can also indicate the geological history of the geode. While unique colors can be mesmerizing, they serve educational purposes as well. Recognizing which minerals contribute to specific colors can enhance children’s understanding of mineralogy. Children can compare the colors of different geodes, fostering a deeper connection to the geological processes behind each one.
"By understanding the external characteristics of geodes, young explorers not only learn about geology but also gain critical observational skills that inspire a lifelong love for science."
In summary, the common external characteristics of geodes reveal much about their origin and the natural processes that created them. Observing their shape, texture, and color can provide valuable educational opportunities, encouraging curiosity and exploration among young science enthusiasts.
Formation of Geodes
Understanding how geodes form is essential in appreciating their beauty and complexity. Geodes are not just random stones; they are products of intricate geological processes. These processes can tell us much about the environment where the geodes were formed. This knowledge adds depth to our understanding of geology and reinforces the connections between natural phenomena and the Earth's history.
Geological Processes Involved
The formation of geodes begins deep within volcanic or sedimentary rocks. This process is largely the result of volcanic activity or mineral-rich groundwater. Geodes typically start as gas bubbles in lava. When the lava cools, these bubbles can become hollow spaces within the rock.
As time passes, minerals dissolved in water seep through these hollow spaces. The conditions within the geode provide a unique environment for mineral growth. There are several key processes at play:

- Cystallization: As the water evaporates, minerals begin to crystallize from the remaining solution. This can create stunning interiors filled with various minerals such as quartz or calcite.
- Sedimentation: In sedimentary environments, layers of minerals can accumulate within a rock formation, further contributing to geode formation.
- Erosion: Over time, geological erosion can expose geodes, making them accessible to explorers.
Each of these stages contributes to the unique characteristics of the finished geode.
Role of Mineral Deposits
Mineral deposits play a pivotal role in the appearance and characteristics of geodes. When water rich in minerals moves through the geode, it carries with it various elements that influence the ultimate look and texture of the geode's interior.
Common minerals found in geodes include:
- Quartz: Often appears as clear or smoky crystals, adding sparkle.
- Amethyst: This purple variety of quartz gives a distinctive color.
- Calcite: Known for its clear to white crystals, it can add a bright tone to the interior.
The combination of these minerals can vary widely depending on local geological conditions. In some cases, this leads to rare geode types. For example, agate geodes will be banded due to the layered deposition of minerals. The study of these mineral deposits is critical for understanding not just the geodes themselves but also the broader context of earth sciences.
"Geodes serve as a window into the geological history of an area, revealing the environment in which they were formed."
Overall, the formation of geodes is a testament to the dynamic processes of our planet. The processes involved lay the foundation for the beauty and variety found in geodes today.
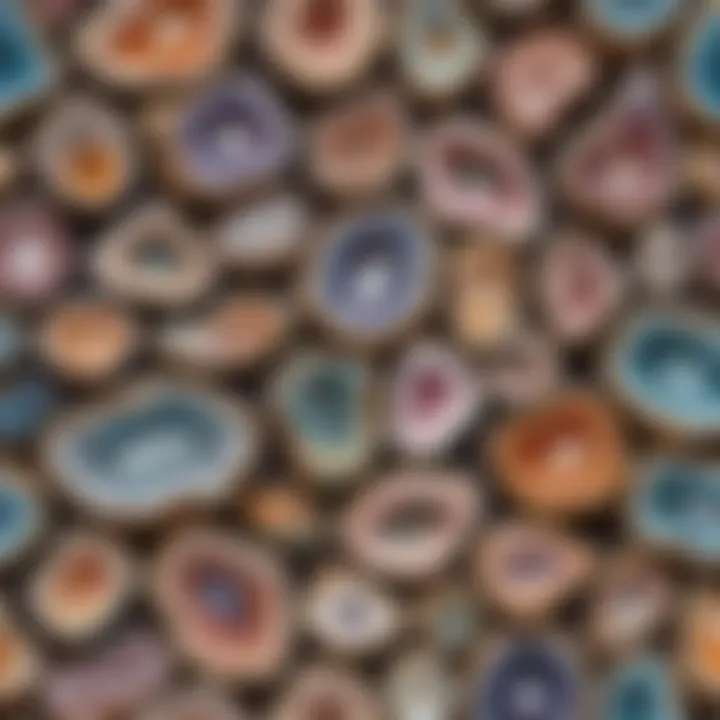
Types of Geodes Based on Appearance
The appearance of geodes provides significant insights into their formation and the environment in which they were created. Understanding the various types of geodes helps geology enthusiasts appreciate the diversity within these remarkable rocks. Each type has its own unique characteristics, making them essential in both educational and scientific contexts. By exploring these types, one can learn more about mineral composition and geological history.
Common Types of Geodes
Amethyst Geodes
Amethyst geodes are widely recognized for their striking purple crystals. This characteristic is due to the presence of iron impurities and the exposure of quartz to radiation. These geodes often attract collectors and enthusiasts, making them a popular choice in various settings.
The key characteristic of amethyst geodes is their deep purple color, which can range from light lavender to dark violet. Because of their beauty, they are often used as decorative items or in jewelry. Their unique feature lies in the stunning crystalline structure that forms inside the geode, which makes them attractive not only visually but also culturally. Collectors value amethyst geodes not just for their aesthetics, but also for their purported metaphysical properties. They are thought to promote tranquility and balance, adding to their allure. However, they can sometimes be more expensive than other types due to their popularity, which could be a disadvantage for some.
Quartz Geodes
Quartz geodes are among the most common types found and are essential in understanding the general geology of the area. They typically contain a significant amount of quartz crystals that form an inner layer within the geode. Their transparency and clarity are distinguishing traits.
The main characteristic of quartz geodes is their versatility. They come in various sizes and can be found in many parts of the world. Quartz is abundant and its crystal structure is relatively simple, making it a favorite in scientific studies. Their unique feature is the ability to form in different environments, leading to a variety of geological formations. However, they may lack the vivid color of others, making them less visually striking in direct comparison. Still, their widespread availability and scientific importance make them a beneficial choice in any educational context.
Calcite Geodes
Calcite geodes feature a distinctive calcite crystal structure, often showcasing a range of colors from clear to shades of white and orange. This variety occurs due to the presence of other minerals and impurities.
Calcite's key characteristic is its crystal formation, which can appear in many forms such as rhombohedral or scalenohedral shapes. This diversity in shapes contributes to their educational value. They are also significant in geological studies because they can shed light on the conditions under which they formed. A unique feature of calcite geodes is their degree of
Practical Observations of Geodes
Understanding how to observe and interact with geodes is vital. It allows us to gather a wealth of information about their formation, structures, and more. Practical observations help cultivate a deeper appreciation for geology and its hidden treasures. Young explorers can benefit greatly from knowing distinct characteristics of geodes. This knowledge can ignite curiosity and promote hands-on exploration.
How to Identify Geodes?
Identifying geodes may seem challenging at first, but some specific features make it easier. A geode generally appears as a rounded rock formation, often resembling a small, bumpy sphere. The outside is usually rough or knobbly, with a hard brown or gray crust. Learning to identify these features is essential for any budding geologist.
- Shape: Look for oval or spherical stones. They often stand out from other rocks due to their unique shapes.
- Texture: Rubbing your fingers on the surface can reveal a rough texture. Some geodes may have little bumps or ridges.
- Size: They can vary in size, but many are small, fitting comfortably in your hand.
- Weight: Geodes are generally heavier than they appear, especially if they contain mineral deposits inside.
Experiencing these characteristics firsthand can significantly improve the learning process.
Field Tips for Young Explorers


Exploring the outdoors, especially in search of geodes, can be quite exciting. However, there are a few tips young adventurers should keep in mind to ensure a safe and fruitful expedition.
- Know where to look: Research areas where geodes are commonly found. Many can be discovered in volcanic or sedimentary rock regions. Local geology books or online sources can provide useful insight.
- Bring the right tools: Always carry basic tools like gloves, a small hammer, and a safety goggles. This is not just for safety, but also for ease when cracking open geodes later on.
- Be observant: Take time to look around. Sometimes, geodes can blend into the surrounding rocks. Focus on shape and color.
- Practice patience: Not every outing will result in a geode discovery. Embrace the journey and enjoy gathering knowledge instead.
"Exploration is the best way to learn; every rock tells a story."
By applying these tips and practices, young geology enthusiasts can sharpen their observational skills. The more they engage with the natural world, the greater their appreciation for its complexities.
Significance of Geode Appearance in Science
Geodes are more than just colorful rocks. Their appearance holds valuable clues about the earth and its processes. Understanding what geodes look like can help scientists and students learn about geological history. Each unique feature, such as color and texture, can indicate different minerals and environmental conditions present when the geode formed. This knowledge can enhance our grasp of geological formations and the evolution of the earth's crust.
Geodes in Geological Studies
When scientists study geodes, they often start by looking at their external characteristics. Outward appearances give hints about what is inside. For example, the formation of certain minerals like quartz or calcite inside geodes can show how long water was present in the cavity during formation. If a geode has a rough surface, it might suggest a different minerals compared to one that is smooth. Such information is important for understanding the earth's past environments.
Additionally, geodes can show variations across different locations. Comparing geodes from various regions allows geologists to draw conclusions about the local geology. By studying these rock formations, they can better understand larger geological processes, such as volcanic activity or sedimentation patterns.
"Through the analysis of geodes, we gain insights into the intricate processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years."
Cultural and Historical Relevance
Geodes are not just crucial in science; they also carry cultural significance. For many societies throughout history, rocks and minerals have been part of their beliefs and traditions. Geodes inspired stories of mystery and wonder. Their hidden beauty inside represented deep wisdom. This connection to culture educated people about the earth's resources.
In today's world, people often collect geodes for their beauty and rarity. This practice can promote interest in geology and natural sciences. Schools and science clubs frequently organize trips to explore local geode sites, stimulating curiosity among children. By engaging with geodes, young learners can appreciate how natural formations tie into broader cultural stories and history.
Understanding geodes provides an educational opportunity linking science and culture, thus enhancing the learning experience for children and nurturing their fascination with the world around them.
Care and Preservation of Geodes
Taking care of geodes is vital for ensuring their beauty and longevity. Geodes are not just fascinating natural formations; they are also delicate and can be damaged without proper handling. Understanding how to care for and preserve these unique specimens helps in maintaining their aesthetic appeal as well as their educational value. For young explorers and their guardians, knowing the proper techniques provides a respectful way to enjoy these geological wonders.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Keeping geodes clean is essential. Dust and dirt can dull their shine and obstruct their natural beauty. Here are some helpful tips for cleaning geodes:
- Gentle Cleaning: Use a soft brush, like a paintbrush, to remove any loose dirt from the exterior. This prevents scratching the surface.
- Mild Soap Solution: For more stubborn dirt, create a solution of warm water and mild dish soap. Dampen a cloth and gently wipe the surface. Avoid soaking, as water can seep into cracks.
- Rinsing: After cleaning with soap, rinse lightly with water. Use a soft cloth to dry completely. This helps to remove any remaining soap residue.
- Polishing: If geodes are polished, you can use a special polish designed for gemstones. Apply it sparingly and polish gently to avoid damage.
Keeping geodes clean ensures they stay attractive, whether displayed at home or for educational projects at school.
Storage Recommendations
Proper storage is crucial for preserving geodes. The right conditions can prevent damage and maintain their appearance over time. Here are some important recommendations for storing geodes:
- Temperature and Humidity: Store geodes in a cool, dry place. Extreme temperatures and high humidity can cause damage to the minerals inside.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: UV rays can fade the colors in certain types of geodes. Keep them away from direct sunlight to prevent discoloration.
- Use Soft Materials: Store geodes in a padded container or wrapped in soft cloth. This protects them from scratches and impacts.
- Display Safely: If displaying geodes, use sturdy shelves and ensure they are secure. Avoid overcrowding, as this can lead to accidents and breakage.
- Regular Checks: Periodically check the condition of the geodes. This way, any signs of damage can be addressed quickly.
By following these storage recommendations, geodes can remain safe and beautiful for many years.
"The beauty of geodes lies not only in their appearance but also in the stories they tell about our planet's history. Caring for them is an investment in that story."
Taking the time to understand the care and preservation of geodes allows young enthusiasts to cultivate a deeper appreciation for geology. This not only encourages responsible collecting but also enriches their educational experience.
The End
Understanding the external features of geodes is essential for those interested in geology. It helps to appreciate not just their physical beauty but also the natural processes that create them. This article has emphasized the importance of observing these structures in detail. Recognizing the significance of elements like shape, size, and surface texture can enhance one's ability to identify and appreciate geodes. Knowledge about geodes can spark curiosity and inspire new interests in science among young learners.
Key Takeaways
- Geodes come in various shapes and sizes, making each unique.
- Understanding their external characteristics can reveal their formation history.
- Geodes are not just rocks; they are pieces of natural history.
- Maintenance and care are necessary for preserving their beauty.
Encouragement for Further Exploration
Exploration should not stop here. There is a world full of geological wonders waiting to be discovered. Young enthusiasts are encouraged to collect their own geodes, explore rocks, and learn about other minerals. Consider visiting geological sites or local museums that feature geodes and minerals. Resources such as Wikipedia or Britannica can provide further insights. Join geology clubs or attend workshops to share discoveries and learn more together. The journey into geology is exciting and full of discovery.







