Unveiling the Intricacies of Left and Right Brain Functions
Science Fun Facts
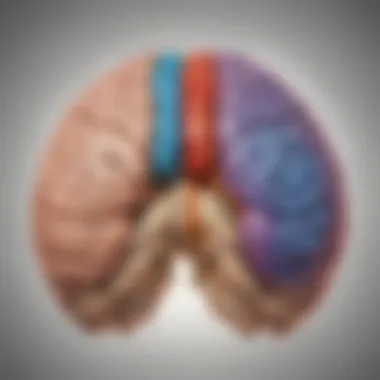
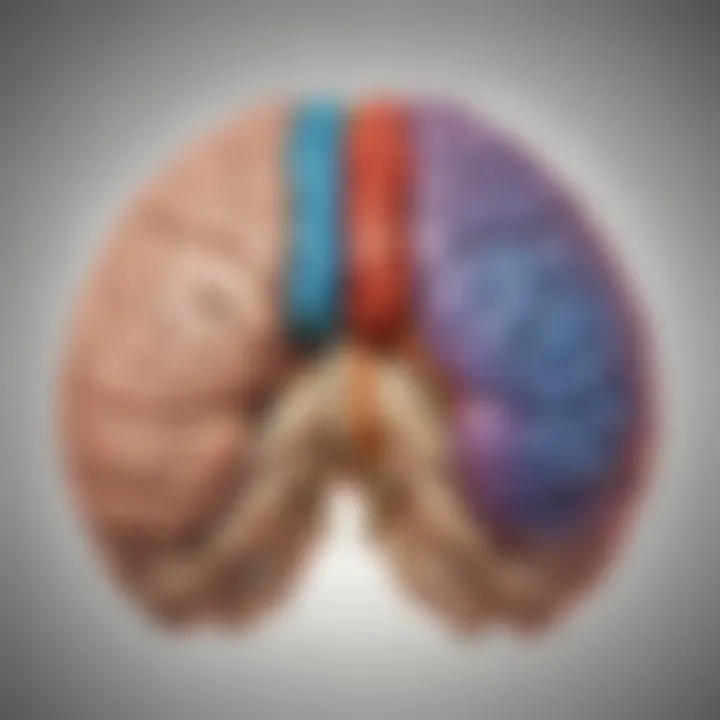
The human brain, an astonishing organ, is divided into two main hemispheres - the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. Each hemisphere has its own distinct functions and specialties. The left hemisphere is typically associated with logical thinking, language processing, and analytical tasks, while the right hemisphere is often linked to creativity, intuition, and spatial awareness. This segregation of functions between the two hemispheres highlights the complexity and sophistication of the human brain. Did you know that the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body, and vice versa?
Discover the Wonders of Science
Exploring the interactions between the left and right brain can offer valuable insights into how we perceive the world and make sense of our experiences. By understanding the unique roles of each hemisphere, we can appreciate the harmonious teamwork that occurs in our brains every day. Imagine watching a captivating movie - the left hemisphere might analyze the dialogue and plot, while the right hemisphere processes the emotions and visual elements, creating a holistic viewing experience. This intricate interplay showcases the brain's exquisite ability to process diverse information simultaneously, resulting in a rich tapestry of perceptions.
Science Quiz Time
Engage in an interactive quiz to test your knowledge about the left and right brain functions. Explore multiple-choice questions that challenge your understanding of brain lateralization. For example, which hemisphere is primarily responsible for recognizing faces? How does handedness relate to brain hemisphere dominance? These brain teasers not only stimulate critical thinking but also deepen your comprehension of the complexities of cognitive functions. By gamifying the learning process, quizzes make education entertaining and rewarding, expanding your cognitive horizons in the realm of neuroscience.
Science Experiment Showcase
Embark on a fun and immersive science experiment to witness the left and right brain functions in action. Follow step-by-step instructions to conduct an experiment that demonstrates the unique strengths of each hemisphere. Gather materials such as color cards, music clips, and tactile objects to engage both hemispheres in various sensory tasks. By actively participating in these experiments, you'll gain hands-on experience in exploring the fascinating world of brain lateralization. Remember to prioritize safety by following precautionary measures and enjoying the journey of discovery in understanding the left and right brain dynamics.
Introduction to Brain Hemispheres
In the exploration of brain functions, understanding the interaction between the left and right hemispheres is crucial. Brain lateralization plays a pivotal role in cognition and behavior, shaping how individuals perceive and process information. By dissecting the nuanced differences between the two hemispheres, a deeper comprehension of human thought processes unfolds. This section serves as the foundational framework for unraveling the intricacies of brain hemisphere dominance and its implications on overall brain functionality.
Overview of Brain Hemispheres
Defining the Left and Right Brain:
A fundamental aspect of comprehending brain functions is to delineate the roles of the left and right hemispheres. The concept of left-brain dominance in logical and analytical thinking contrasts with right-brain dominance in creativity and intuition. This distinction influences an individual's cognitive preferences and problem-solving approaches significantly, shedding light on the diverse capabilities of each hemisphere. Understanding the unique functions attributed to each side enhances our grasp of human cognitive diversity and neural processing mechanisms.
Historical Perspectives on Brain Lateralization:
Exploring the historical evolution of brain lateralization provides valuable insights into how scientific understanding has progressed over time. From early theories proposing distinct functions for each hemisphere to contemporary research confirming the interconnectivity between the two sides, delving into the historical context enriches our appreciation of brain function complexity. The development of brain lateralization theories reflects the continuous refinement of neuroscientific knowledge and the ongoing quest to unravel the mysteries of human cognition.
Brain Hemisphere Dominance
Functions Associated with Each Hemisphere:
Examining the specific functions linked to each hemisphere elucidates the specialization that occurs within the brain. The left hemisphere, known for its linguistic and analytical capacities, contrasts with the right hemisphere's prowess in spatial perception and emotional processing. Understanding the distinct contributions of each side provides a comprehensive view of how neural networks govern cognition and behavior, unveiling the intricate balance required for optimal brain functionality.
Implications of Hemisphere Dominance:
The implications of hemispheric dominance extend beyond mere cognitive abilities to influence individual strengths and preferences. While left-brain dominance may signify proficiency in logical reasoning, right-brain dominance highlights skills in creativity and holistic thinking. Acknowledging the implications of this dominance offers valuable insights into how individuals perceive the world and tackle various challenges, showcasing the multidimensional nature of human cognition.
Myth vs. Reality
Debunking Common Misconceptions:
Addressing prevalent myths surrounding left and right brain functions is essential to dispel misconceptions that oversimplify brain lateralization. By debunking common stereotypes attributing personality traits solely to one hemisphere, a more nuanced understanding of brain complexity emerges. This nuanced approach challenges oversimplified views of brain function, emphasizing the need to embrace the sophisticated interplay between both hemispheres for a holistic perspective on cognitive processes.
Clarifying the Left-Brain, Right-Brain Myth:
Clarifying misconceptions related to the left-brain, right-brain myth involves untangling popular beliefs from empirical evidence. While certain tasks may activate specific brain regions more prominently, the brain functions as an integrated whole rather than segregated halves. Clarifying this myth highlights the need to appreciate the brain's holistic nature, where both hemispheres collaborate seamlessly to facilitate various cognitive functions. By emphasizing the interconnectivity between the left and right hemispheres, this clarification underscores the complexity of brain processing and the fallacy of oversimplified categorizations.
Distinct Functions of the Left Brain
In this section, we delve into the distinct functions of the left hemisphere of the brain, unraveling a myriad of essential cognitive processes that define our analytical and logical capabilities. The elucidation of these functions is crucial to grasp the complexity of brain lateralization and its implications for human cognition and behavior. By shedding light on the specific elements, benefits, and considerations surrounding the distinct functions of the left brain, we pave the way for a deeper understanding of how this hemisphere contributes to our everyday thinking and decision-making.
Analytical and Logical Thinking
Language Processing
Language processing, a cornerstone of left-brain functionality, plays a pivotal role in our ability to communicate, comprehend, and express ideas effectively. This intricate cognitive process involves the decoding and interpretation of linguistic information, enabling us to engage in spoken and written communication effortlessly. The key characteristic of language processing lies in its systematic nature, where words and sentences are structured coherently to convey meaning. This analytical approach to language fosters clear communication and logical reasoning, making it a valuable asset in various contexts, including academic pursuits, professional settings, and social interactions.
Mathematical Abilities
Mathematical abilities, another hallmark of left-brain dominance, are instrumental in problem-solving, quantitative reasoning, and numerical proficiency. The essence of mathematical cognition revolves around logical deductions, numerical operations, and spatial reasoning, making it a preferred choice for analytical tasks requiring precision and accuracy. The unique feature of mathematical abilities lies in their adaptability across diverse domains, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex calculus, offering a versatile toolkit for navigating real-world challenges. While the advantages of strong mathematical skills are evident in academic achievements and critical thinking, potential disadvantages may arise from overemphasis on quantitative analysis at the expense of holistic problem-solving approaches.
Sequential Processing
Problem-Solving Skills
The prowess of left-brain sequential processing shines through in our problem-solving competencies, enabling us to deconstruct complex issues into manageable steps and devise effective solutions. Problem-solving skills rely on systematic reasoning, logical deductions, and structured approaches to tackle challenges methodically. The key characteristic of problem-solving lies in its emphasis on analytical thinking, where individuals leverage data, patterns, and logic to unravel intricate problems and derive optimal solutions. While the structured nature of problem-solving enhances efficiency and effectiveness in decision-making, potential drawbacks may include rigidity in approaching dynamic or ill-defined problems.
Detail Orientation
Detail orientation, a fundamental aspect of left-brain processing, underscores our ability to focus on specific elements, analyze intricate information, and maintain precision in tasks. This meticulous attention to detail involves scrutinizing data, recognizing patterns, and ensuring accuracy in processes, fostering a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. The unique feature of detail orientation lies in its role in enhancing thoroughness and quality assurance, particularly in tasks demanding precision and consistency. While the advantages of being detail-oriented are evident in error reduction and quality control, there may be challenges associated with potential tunnel vision or overlooking broader contextual insights.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning
Decision-Making Processes
Decision-making processes, a critical facet of left-brain functionality, govern our ability to evaluate options, weigh consequences, and make informed choices based on rational assessments. The essence of decision-making lies in combining analytical insights with emotional considerations to arrive at optimal decisions that align with our goals and values. The key characteristic of decision-making processes resides in their emphasis on logic, evidence evaluation, and risk assessment, offering a structured framework for navigating complex dilemmas. While the structured approach enhances clarity and objectivity in decision-making, potential disadvantages may stem from over-reliance on data-driven decisions at the expense of intuitive judgments.
Evidence-Based Judgments
Evidence-based judgments, a cornerstone of critical thinking in the left brain, involve evaluating information, scrutinizing evidence, and drawing reasoned conclusions supported by empirical data. This analytical process hinges on logical reasoning, hypothesis testing, and inference drawing to form well-informed judgments grounded in evidence. The unique feature of evidence-based judgments lies in their emphasis on objectivity and credibility, fostering trustworthy decision-making and cognitive clarity. While the advantages of relying on evidence are evident in informed choices and rational assessments, potential challenges may arise from information overload or the complexities of integrating diverse sources into coherent judgments.
Distinct Functions of the Right Brain
In the realm of understanding the left and right brain functions, the section dissecting the Distinct Functions of the Right 🧠 Brain stands out as a pivotal exploration. This segment delves into the unique responsibilities of the right hemisphere, enriching our comprehension of cognitive processes. By highlighting the specific elements associated with the right brain's functionality, a profound insight into its benefits and considerations within the context of brain lateralization emerges. It illuminates how the right brain contributes to our holistic cognitive functioning, emphasizing its role in creative, intuitive, and emotive processes alongside its counterpart, the left brain.
Creative and Intuitive Thinking
Artistic Expression
Discussing the facet of Artistic Expression within the domain of the right brain's functions uncovers a profound aspect of human cognition. Artistic Expression holds paramount significance in this detailed analysis due to its intrinsic link to imagination, creativity, and emotional depth. The key characteristic of Artistic Expression lies in its ability to transcend verbal language and communicate complex emotions and concepts through various artistic mediums. This choice resonates deeply within this article as it mirrors the intricate workings of the right brain, known for its non-linear thinking and emotional processing. The unique feature of Artistic Expression lies in its power to evoke empathy, provoke thought, and stimulate multiple cognitive domains simultaneously, contributing significantly to the multifaceted analysis of brain lateralization.
Imagination and Innovation
Exploring Imagination and Innovation within the realm of the right brain's functions provides a gateway to understanding cognitive flexibility and originality. Imagination and Innovation play a vital role in nurturing creativity, problem-solving skills, and adaptive thinking processes essential for human advancement. The key characteristic of Imagination and Innovation lies in their capacity to envision possibilities, challenge existing paradigms, and drive progress through novel ideas and solutions. This choice resonates strongly within this article as it aligns with the broader theme of cognitive exploration and the dynamic interplay between creativity and logical reasoning. The unique feature of Imagination and Innovation lies in their potential to inspire growth, foster resilience, and spark revolutionary changes in cognitive landscapes.
Holistic Processing


Pattern Recognition
Delving into Pattern Recognition within the holistic processing domain illuminates a fundamental aspect of cognitive perception and organization. Pattern Recognition plays a crucial role in identifying relationships, structures, and meaningful connections within a complex array of information. The key characteristic of Pattern Recognition lies in its ability to streamline cognitive processes, enhance learning efficiency, and facilitate decision-making through pattern-based algorithms. This choice is particularly relevant to this article as it mirrors the intricate parallelism between the right brain's intuitive insight and the left brain's analytical prowess. The unique feature of Pattern Recognition lies in its capacity to detect subtle nuances, anticipate trends, and adapt cognitive strategies based on evolving patterns, enriching the narrative of brain lateralization.
Emotional Intelligence
Exploring Emotional Intelligence within the holistic processing domain unveils a critical component of social cognition and emotional well-being. Emotional Intelligence plays a pivotal role in managing interpersonal relationships, understanding individual emotions, and navigating social dynamics effectively. The key characteristic of Emotional Intelligence lies in its capacity to empathize, communicate with empathy, and regulate emotions for constructive interactions. This choice resonates profoundly within this article as it aligns with the essence of human interaction, empathy, and emotional depth, highlighting the significance of emotional awareness in cognitive processes. The unique feature of Emotional Intelligence lies in its ability to cultivate empathy, foster resilience, and promote harmonious interpersonal connections, adding depth to the discourse on brain lateralization.
Interplay Between the Hemispheres
In this perceptive exploration of 'Interplay Between the Hemispheres,' we unravel the intricate connections and dependencies that underpin the brain's functional dynamics. The symbiotic relationship between the left and right brain hemispheres forms the backbone of cognitive processing and decision-making, shaping our daily interactions and thought processes. By dissecting the interplay between these hemispheres, we gain profound insights into how information flows seamlessly between analytical reasoning and creative expression. This section elucidates the significance of understanding the 'Interplay Between the Hemispheres' in deciphering the complexities of human cognition, emotion, and behavior.
Communication and Integration
Corpus Callusom Function
Diving into the core of brain connectivity, the Corpus Callusom plays a pivotal role in facilitating inter-hemispheric communication and information exchange. This specialized structure acts as a bridge between the left and right brain, allowing for the seamless transfer of neuronal signals essential for coordinated cognitive processes. The unique characteristic of Corpus Callusom lies in its ability to synchronize cognitive functions, ensuring a harmonious integration of logical reasoning and creative thinking. Its strategic function in this article underscores its paramount importance in elucidating how cognitive processes are coordinated and harmonized to optimize brain functionality.
Coordination of Cognitive Processing
Exploring the intricacies of 'Coordination of Cognitive Processing,' we delve into how the brain manages and orchestrates multifaceted tasks through synchronized neural networks. This aspect highlights the brain's remarkable capacity to manage divergent cognitive functions effectively, ranging from attention to memory and decision-making. The key feature of Cognitive Coordination lies in its adaptability and versatility, facilitating fluid transitions between different cognitive domains based on task demands. This functionality enriches this article by showcasing how cognitive processes are orchestrated and streamlined to enhance overall cognitive efficiency efficiently.
Synergy in Cognitive Tasks
Brain Hemisphere Synchronisation
Unpacking the significance of 'Brain Hemisphere Synchronization,' we uncover the mechanisms responsible for harmonizing the left and right brain functions for optimal cognitive performance. This synchronized interplay ensures a cohesive balance between creativity and analytical thinking, fostering holistic problem-solving and innovative ideation. The hallmark characteristic of Brain Hemisphere Synchronization is its ability to promote neural connectivity and information exchange, enabling a synergistic fusion of diverse cognitive abilities essential for complex cognitive tasks. This distinct feature accentuates the pivotal role of synchronization in augmenting cognitive efficiency and adaptability within the cognitive framework of this article.
Enhancement of Cognitive Abilities
Delving into the realm of 'Enhancement of Cognitive Abilities,' we explore how synergistic brain functions heighten cognitive acuity and aptitude across various domains. This aspect underscores the transformative impact of coordinated left and right brain operations on amplifying cognitive performance, enhancing learning retention, and bolstering problem-solving skills. The key highlight of Cognitive Ability Enhancement lies in its capacity to optimize neural pathways and cognitive resources, refining information processing and critical thinking capabilities. This insightful analysis elevates the discussion within this article by illuminating how cognitive abilities are consolidated and enhanced through synchronized brain activities.
Role in Complex Activities
Music and Language Processing
Considering the intricate role of 'Music and Language Processing,' we unravel the profound impact of left and right brain synergy on artistic and linguistic proficiencies. This segment underscores how music and language processing engage both hemispheres synergistically, enriching communication skills, creativity, and emotional expression. The distinguishing trait of Music and Language Processing lies in its ability to transcend linguistic and musical barriers, fostering cross-hemispheric collaborations essential for complex cognitive tasks. This detailed exposition adds depth to this article by elucidating how music and language processing interlace to cultivate a holistic approach to cognitive engagement and sensory perception.
Creativity and Problem-Solving
Exploring the confluence of 'Creativity and Problem-Solving,' we unravel the intricate dance between divergent thinking and analytical reasoning to surmount intellectual challenges effectively. This section emphasizes how creative ideation and logical problem-solving collaborate to unlock innovative solutions, propel imaginative thinking, and fuel cognitive flexibility. The central feature of Creativity and Problem-Solving lies in its propensity to foster dynamic brain engagements, nurturing adaptive thinking patterns and resilience in the face of cognitive complexities. This nuanced exploration enriches the narrative of this article by presenting a holistic view of how creativity and problem-solving intertwine to optimize cognitive performance and decision-making processes.
Factors Influencing Brain Lateralization
Brain lateralization is a complex phenomenon influenced by various factors that shape cognitive functions. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial in unraveling the mysteries of the left and right brain. Genetic and environmental influences play pivotal roles in determining hemisphere dominance and cognitive processing. Additionally, neuroplasticity and training can mold brain connectivity, impacting cognitive flexibility. Cultural and educational backgrounds also contribute to brain lateralization through exposure to diverse learning experiences. Exploring these factors provides nuanced insights into how our brains function and adapt.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Innate Brain Hemispheric Dominance
Biological predispositions guide certain individuals towards a dominant brain hemisphere, impacting their cognitive strengths. Whether inherent talents lean towards analytical left-brain abilities or creative right-brain skills, innate hemispheric dominance affects cognitive processing. This natural inclination towards a specific hemisphere can influence learning styles and problem-solving approaches. Acknowledging this intrinsic feature helps individuals harness their cognitive strengths effectively within educational and professional settings.
Developmental Influences
The developmental journey from infancy to adulthood shapes brain connectivity and lateralization patterns. Early life experiences, such as language exposure and sensory stimulation, contribute significantly to brain development. These developmental influences not only impact cognitive functions but also sculpt neural pathways that define individual cognitive styles. Understanding the impact of developmental influences on brain lateralization underscores the importance of early intervention and holistic learning environments for optimal cognitive growth.
Neuroplasticity and Training
Impact of Learning and Practice
Continuous learning and deliberate practice can augment neural connections, enhancing cognitive abilities and reshaping brain functions. The brain's adaptability, known as neuroplasticity, allows for skill acquisition and cognitive improvements through consistent training. By actively engaging in challenging tasks and varied learning experiences, individuals can stimulate neural pathways and promote cognitive flexibility. The impact of learning and practice underscores the importance of lifelong learning for maintaining cognitive vitality.
Brain Plasticity Mechanisms
Brain plasticity encompasses the brain's ability to reorganize its structure in response to learning and experience. This dynamic process enables individuals to adapt to new information, refine skills, and recover from brain injuries. Understanding the mechanisms of brain plasticity sheds light on the potential for cognitive improvement and rehabilitation. By exploring these adaptive processes, researchers can devise innovative interventions for neurorehabilitation and cognitive enhancement.
Cultural and Educational Factors
Educational Curriculum Design
Educational frameworks and teaching methodologies significantly influence brain development and cognitive outcomes. Tailoring educational curricula to accommodate diverse learning styles and cognitive preferences fosters optimal learning environments. By integrating cross-disciplinary activities and interactive learning strategies, educational institutions can promote cognitive growth and creative thinking. The design of educational curricula plays a vital role in shaping individuals' cognitive abilities and preparing them for future academic and professional challenges.
Social Norms and Cognitive Development
Social norms and cultural practices influence cognitive development by shaping individuals' perceptions and behavioral patterns. Societal expectations and norms can either foster or hinder cognitive growth, impacting how individuals navigate complex cognitive tasks. By recognizing the influence of social environments on cognitive development, educators and caregivers can create supportive frameworks that nurture diverse cognitive skills. Addressing the interplay between social norms and cognitive development enriches understanding of how external factors shape internal cognitive processes.
Clinical Implications and Future Research
In delving deep into the intricate workings of the left and right brain hemispheres, it becomes imperative to consider the significant implications that these findings have on clinical practices and future research endeavors. Understanding the specific roles each hemisphere plays in cognition and behavior is crucial for identifying and addressing neurological disorders effectively. By exploring the relationship between brain lateralization and neuropsychological disorders, researchers and clinicians can enhance diagnostic accuracy and tailor treatment strategies to individual patients' needs.
Neuropsychological Disorders
Hemispheric Specialization in Disorders
One key aspect of neuropsychological disorders lies in the specialization of each hemisphere in contributing to specific cognitive functions. The hemispheric specialization in disorders sheds light on how disruptions in these functions can manifest in varying neurological conditions. By focusing on the distinctive characteristics of how each hemisphere processes information and controls behavior, researchers can pinpoint the underlying causes of disorders and develop targeted interventions. The unique feature of hemispheric specialization in disorders lies in its ability to unravel the complexities of brain functioning and unravel the mysteries of cognitive impairments observed in clinical settings. While this specialization offers valuable insights into understanding the brain, it also presents challenges in accurately diagnosing and treating complex neurological conditions.
Therapeutic Interventions
When discussing therapeutic interventions in the context of neuropsychological disorders, it is essential to highlight the diverse approaches available for managing and mitigating cognitive deficits. Therapeutic interventions encompass a wide range of strategies, including pharmacological treatments, cognitive-behavioral therapies, and neurorehabilitation programs. Each intervention is tailored to address specific symptoms associated with different disorders, aiming to improve patients' functional abilities and quality of life. The key characteristic of therapeutic interventions lies in their multifaceted approach to targeting cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects of neurological disorders, offering patients comprehensive support to enhance their overall well-being. While therapeutic interventions provide invaluable assistance to individuals with neuropsychological disorders, challenges may arise in determining the most effective treatment strategies for each patient and ensuring long-term therapeutic success.
Advancements in Brain Imaging
The field of brain imaging has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, revolutionizing the way researchers study brain function and structure. These technological developments play a pivotal role in enhancing our understanding of brain lateralization and its implications for cognition and behavior. By utilizing cutting-edge imaging techniques, such as functional MRI studies, researchers can visualize brain activity in real-time, unveiling the intricate networks and regions responsible for specific cognitive functions. Functional MRI studies offer a non-invasive and precise method of mapping brain activity, providing crucial insights into how each hemisphere contributes to different cognitive processes. Despite its benefits in elucidating brain function, functional MRI studies may face limitations in capturing the nuanced interplay between brain regions and interpreting complex neural networks.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations have sparked a paradigm shift in brain imaging, introducing novel tools and methods that push the boundaries of neuroscientific research. These innovations encompass a wide array of advancements, including high-resolution imaging modalities, artificial intelligence algorithms, and virtual reality platforms tailored for brain mapping. The key characteristic of technological innovations lies in their ability to enhance the spatial and temporal resolution of brain imaging, allowing researchers to explore brain functions at an unprecedented level of detail. By incorporating these innovative technologies into research protocols, scientists can uncover hidden insights into brain lateralization and its impact on cognition and behavior. While technological innovations offer tremendous potential for advancing neuroimaging capabilities, challenges may arise in integrating complex data sets, ensuring data accuracy, and maintaining ethical standards in research practices.
Emerging Trends in Cognitive Neuroscience
The realm of cognitive neuroscience is continuously evolving, driven by emerging trends that shape our understanding of brain function and behavior. These trends illuminate the dynamic interplay between brain hemispheres, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries and paradigm shifts in cognitive research. By exploring cross-hemispheric interactions, researchers can unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying information processing and cognition, leading to novel insights into brain function. Cross-hemispheric interactions highlight the synergistic relationship between the left and right hemispheres, emphasizing the collaborative nature of cognitive processes and the integration of specialized functions across brain regions. While these interactions offer a holistic view of brain functioning, challenges may emerge in deciphering the complexities of neural connectivity and elucidating the underlying mechanisms that govern cognitive processes.
Future Directions in Research
As cognitive neuroscience continues to progress, future research directions hold immense potential for reshaping our understanding of brain lateralization and its implications for human cognition. By examining future directions in research, scientists can anticipate key areas of exploration, including neuroplasticity mechanisms, neural network dynamics, and brain-computer interfaces. These research avenues offer new possibilities for investigating brain function at a micro and macro level, unveiling unprecedented insights into the adaptability and plasticity of the human brain. The unique feature of future directions in research lies in their capacity to drive innovation, foster interdisciplinary collaboration, and inspire transformative breakthroughs in cognitive neuroscience. While these developments present exciting opportunities for advancing our knowledge of the brain, challenges may arise in translating research findings into clinical applications and addressing ethical considerations in neuroscientific inquiry.







